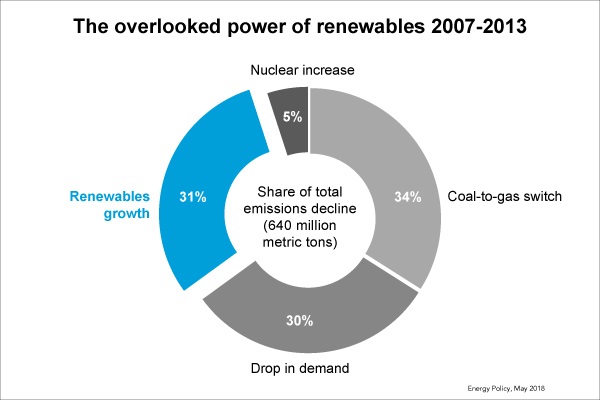
Image: The overlooked power of renewables 2007-2013: From Environmental Defense Fund
This lecture is an introduction to energy production and use and their relation to climate change.
In this lecture, “energy” is the energy we use as a society. That is, usable heat or power or a source of usable power, such as fossil fuels, wind, and solar.
The purpose of this lecture is to introduce the energy landscape and what we need to address to reduce carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels as well as the status and the growing importance of renewables.
This lecture was given at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The pandemic may have important consequences on our energy future. There will definitely be a “recession-like” reduction of emissions. But what happens afterwards is not easy to project. Fossil fuels will be cheap, hence, appealing. It is, also, an opportunity for renewables to assume a larger portion of the energy portfolio. As people, governments, non-governmental organizations, and corporations position themselves, there will be a complicated combination of all possibilities.
The lecture includes:
- Recap of carbon dioxide emissions
- Trajectory
- Sources
- Stating the direct relation between fossil fuel energy use climate change
- Examination and analysis of the world’s primary energy supply from 1973 to 2018 (most recent data at the time of lecture)
- Point: Globally, energy demand continues to increase
- Point: The persistence of fossil fuels in the world’s energy supply
- Point: Recent developments in renewable energy
- Summary of relation between (reference to previous lecture)
- Climate
- Energy
- Population
- Consumption
- Societal Success
In is often better to download the lecture rather than listening in the preview.
Link to lecture (~32 minutes)
A good complement to this lecture is this one on Framing Approaches to Climate Change Problem Solving
Reference Materials:
Class:
International Energy Agency (IES) Data and Statistics, (accessed 29 March 2020)
- Slides in lecture:
- Energy topic = “Energy supply”
- Indicator = “Energy generation by source”
- Country or region = “World,” “United States,” China
Clean energy boom played key role in recent US carbon emissions drop, study shows, Mohlin (2018)
General References:
- International Energy Agency: A go to source.
- U.S. Energy Information Administration: Another go to source.
Rood’s references
- OpenClimate tagged climate-and-energy
- OpenClimate tagged carbon-dioxide (contains news on emissions)
Some old Rood Blog’s (links may not work, and there is little I can do about it)
- We like to burn things
- Energy Security – All the Oil We Want
- No Energy Policy and Even Less Climate Policy
- Earthquakes and Climate Change